在使用 Mabatis 时往往需要有成对出现的 .java 后缀格式 Mapper 接口文件及 .xml 后缀格式的 XML 文件,其中 XML 文件放在资源目录,而 Java 文件自然放在运行目录,通过调用 Mapper 接口中定义的方法就能触发到其通过 namespace 关联的 XML 文件中的 SQL 语句,从而实现了业务逻辑与数据库交互的解耦,避免像传统 JDBC 编程那样在 Java 代码中写 SQL 与数据库交互,那么 Mybtis 是怎么将 Mapper 接口方法与 XML 中 SQL 语句进行绑定与触发的呢?下面我们通过测试方法 debug 调试进行进行代码跟踪。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
public class ProxyTest {
private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ExecutorTest.class);
private Configuration configuration;
private Connection connection;
private JdbcTransaction jdbcTransaction;
private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
@Before
public void init() throws SQLException {
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder factoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
sqlSessionFactory = factoryBuilder.build(ExecutorTest.class.getResourceAsStream("/mybatis/mybatis-config.xml"));
configuration = sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration();
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(JDBC.url, JDBC.username, JDBC.password);
jdbcTransaction = new JdbcTransaction(connection);
}
@Test
public void testProxy() throws SQLException {
try (SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User user = userMapper.selectUser(1);
System.out.println("User : " + user);
}
}
}
|
Mapper 接口注册
首先在 ProxyTest#init 方法中会触发 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder#build 方法进行配置文件解析,SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 顾名思义是 SqlSessionFactory 构造器,SqlSessionFactory 是生产 SqlSession 的工厂,SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 通过解析配置信息构造具体相应特性的 SqlSessionFactory,从而生产具有不同特性的 SqlSession 对象。按我理解,不同的特性,归根到底体现在 Configuration 对象的差异。
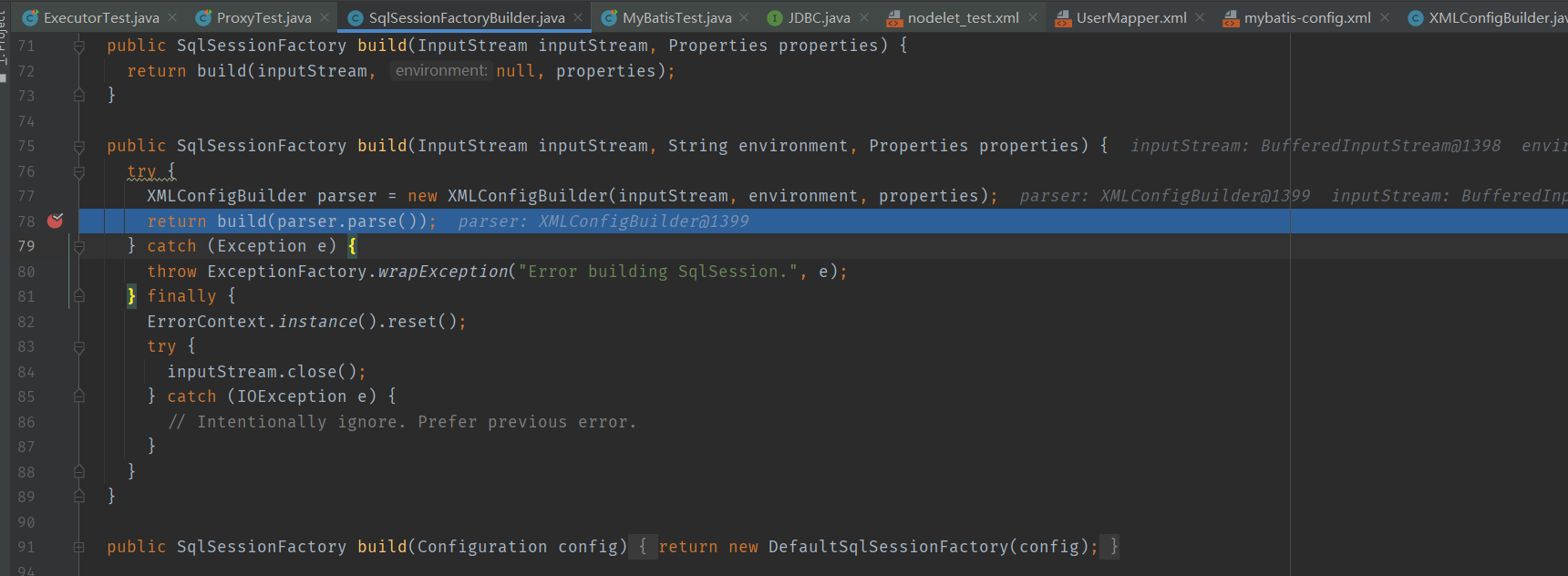
XMLConfigBuilder 的 parseConfiguration 方法会解析 XML 文件中的各种标签,其中包括 mappers 标签。
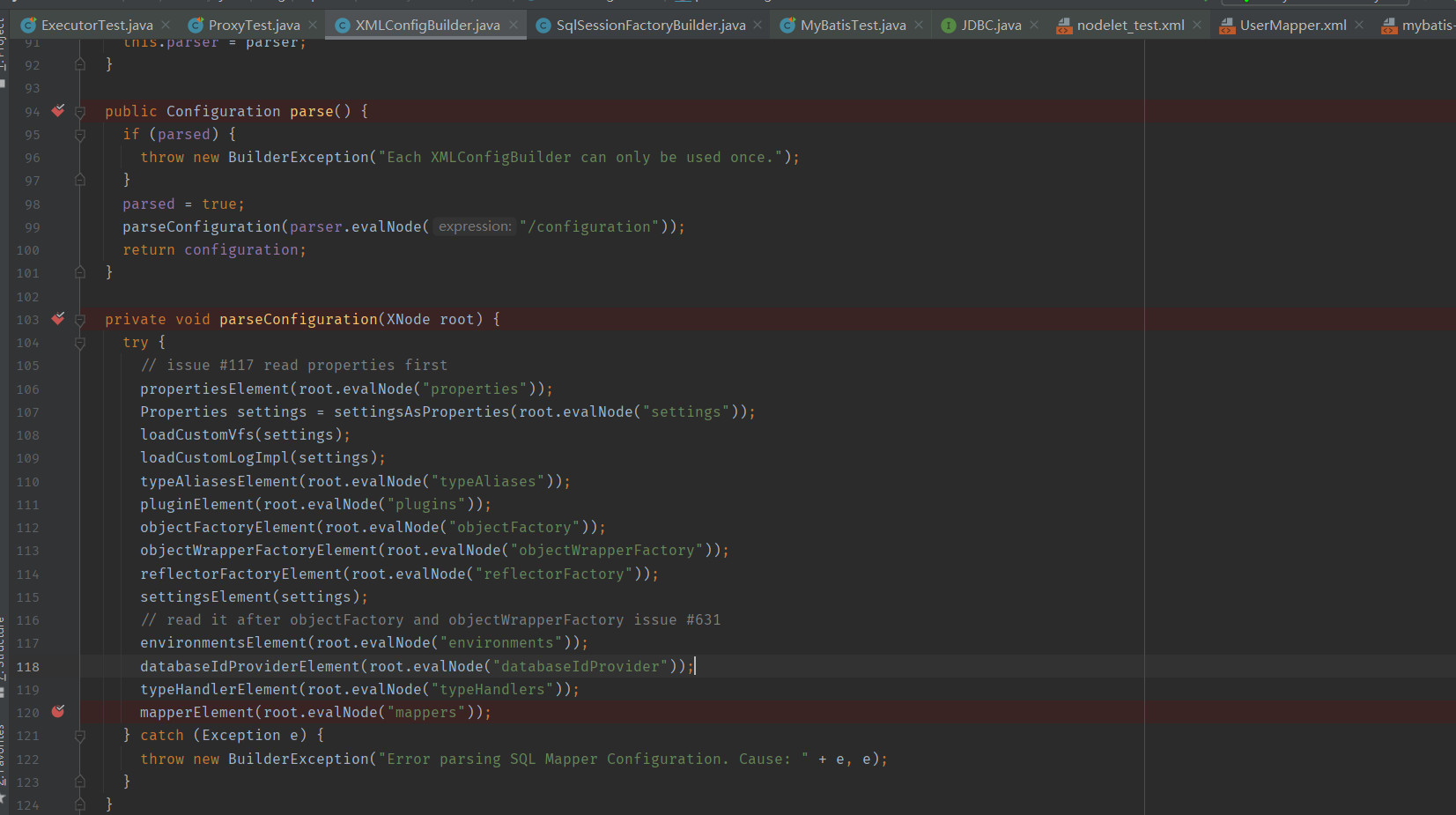
在 mapperElement 方法中会匹配 mapper 的配置方式,然后根据不同方式去读取 Mapper 的内容,
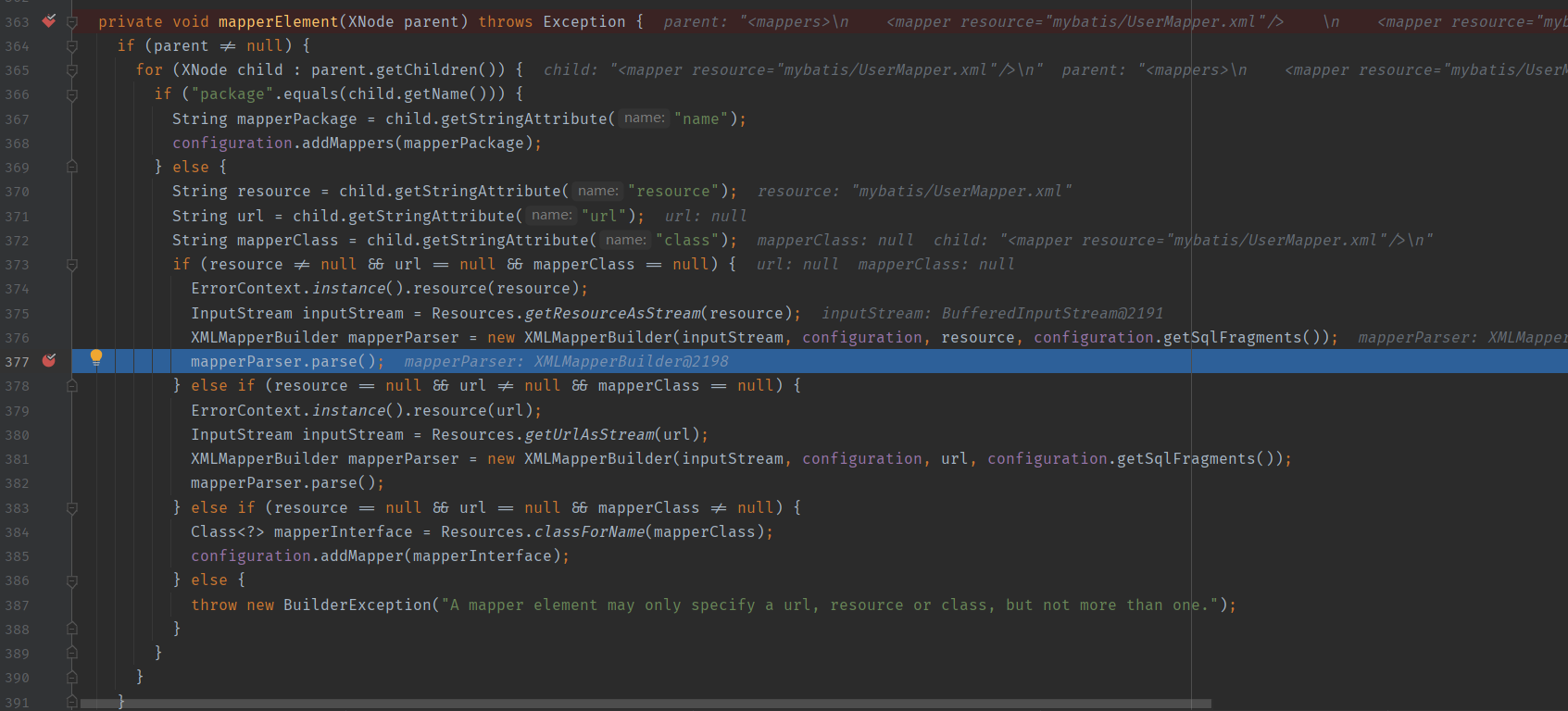
由于我在 mavatis-config.xml 中以 resource 属性指定 mapper 的 XML 文件,所以上述代码会进入第一个 if 分支,以 resource 方式构造 XMLMapperBuilder 对象,然后进入 XMLMapperBuilder 的 parse 方法。
1
2
3
4
|
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mybatis/UserMapper.xml"/>
<mapper resource="mybatis/ContainerMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
|
XMLMapperBuilder 的 parse 方法
这个方法主要有关键的两步,第一步是解析 mapper 文件中的各个 SQL 相关的标签,最终整合成一个类似 <标签id,Statement> 之类的映射表,第二步是为Mapper 绑定代理工厂。
当触发 Mapper 方法时会通过 Mapper 的 Class 信息获取代理工厂并生成代理对象,这个代理对象中会缓存 mapper 方法与具体方法调用器的关系,类似 <method, invoker> 之类的映射,具体的触发逻辑交给相应的 invoker 实现,invoker 会使用到前面第一步中缓存的 <标签id,Statement> 的映射,拿到方法对应的 Statement 就能触发相应的 SQL 指令了。下面我们先看前两步。
解析与配置 Statement
XMLMapperBuilder#configurationElement 方法解析 mapper 节点信息
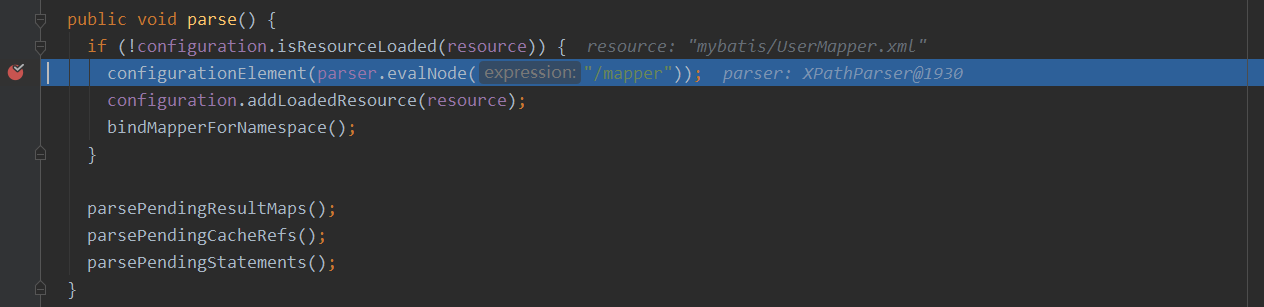
XMLMapperBuilder#configurationElement 方法中调用 XMLMapperBuilder#buildStatementFromContext 方法解析一个 mapper 文件中所有的 SQL 语句对应的节点,然后在复写方法中遍历节点集,然后为每个节点创建一个 XMLStatementBuilder 去解析其中的内容,得到一个对应的 MappedStatement 。
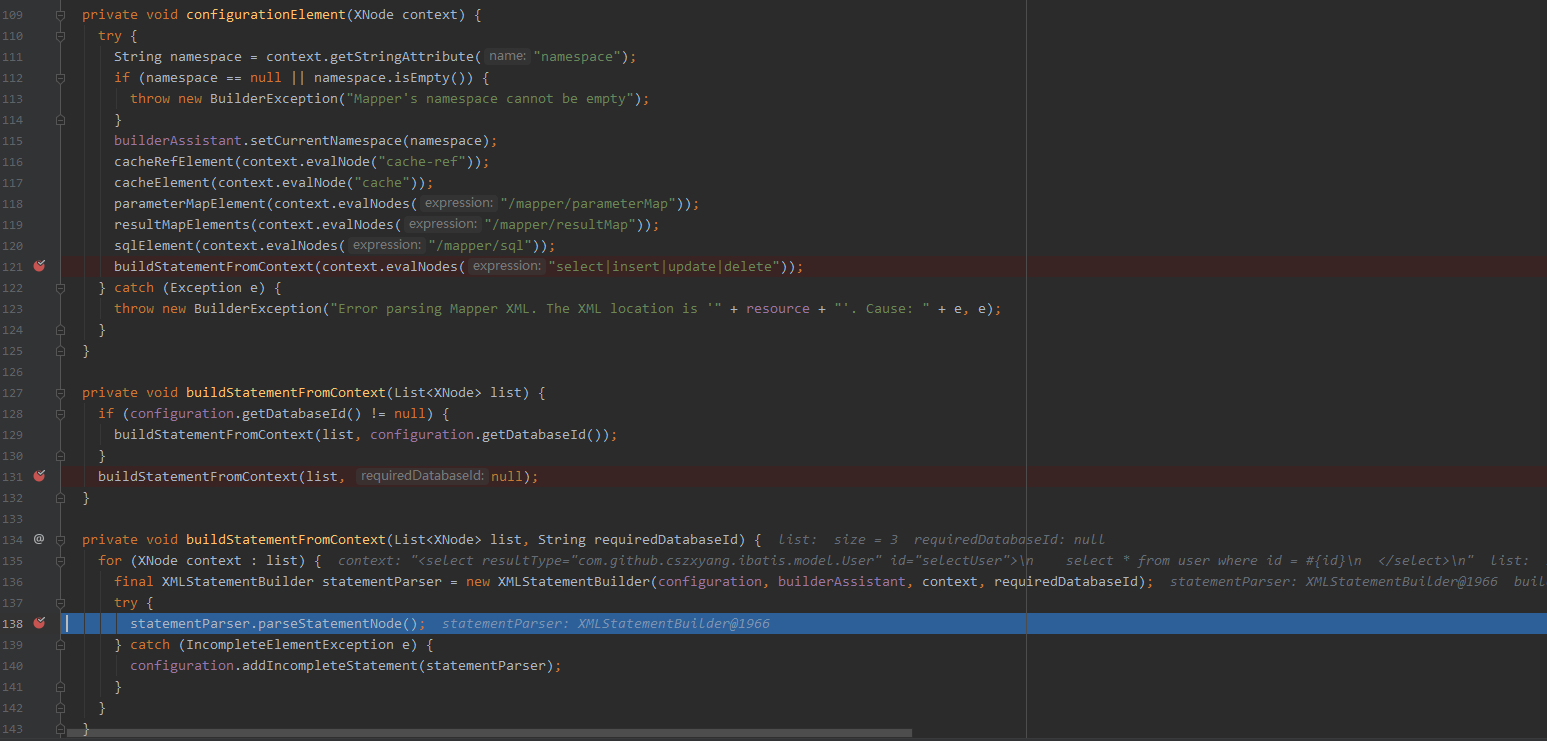
parseStatementNode 方法顾名思义就是解析一个 XML 语句标签的内容,得到一个 MappedStatement 对象。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
|
public void parseStatementNode() {
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
if (!databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, this.requiredDatabaseId)) {
return;
}
// select 或 delete 或 update 等
String nodeName = context.getNode().getNodeName();
// SqlCommandType 枚举,对应 DML 类型
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
boolean flushCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("flushCache", !isSelect);
boolean useCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("useCache", isSelect);
boolean resultOrdered = context.getBooleanAttribute("resultOrdered", false);
// Include Fragments before parsing
XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer(configuration, builderAssistant);
includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode());
String parameterType = context.getStringAttribute("parameterType");
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveClass(parameterType);
String lang = context.getStringAttribute("lang");
LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang);
// Parse selectKey after includes and remove them.
processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver);
// Parse the SQL (pre: <selectKey> and <include> were parsed and removed)
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyStatementId = id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX;
keyStatementId = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(keyStatementId, true);
if (configuration.hasKeyGenerator(keyStatementId)) {
keyGenerator = configuration.getKeyGenerator(keyStatementId);
} else {
keyGenerator = context.getBooleanAttribute("useGeneratedKeys",
configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType))
? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
}
// 解析具体的 SQL 语句
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);
StatementType statementType = StatementType.valueOf(context.getStringAttribute("statementType", StatementType.PREPARED.toString()));
Integer fetchSize = context.getIntAttribute("fetchSize");
Integer timeout = context.getIntAttribute("timeout");
String parameterMap = context.getStringAttribute("parameterMap");
String resultType = context.getStringAttribute("resultType");
Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType);
String resultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap");
String resultSetType = context.getStringAttribute("resultSetType");
ResultSetType resultSetTypeEnum = resolveResultSetType(resultSetType);
if (resultSetTypeEnum == null) {
resultSetTypeEnum = configuration.getDefaultResultSetType();
}
String keyProperty = context.getStringAttribute("keyProperty");
String keyColumn = context.getStringAttribute("keyColumn");
String resultSets = context.getStringAttribute("resultSets");
// 通过下面的参数构建 MappedStatement,并添加到 Configuration 的 mappedStatements 映射表中
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,
fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,
resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets);
}
|
MapperBuilderAssistant#addMappedStatement 会将 MappedStatement 添加到 Configuration 的 mappedStatements 映射表中。
比如对于 UserMapper,其 XML 文件内容为
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.github.cszxyang.ibatis.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="selectUser" resultType="com.github.cszxyang.ibatis.model.User">
select * from user where id = #{id}
</select>
<insert id="addUser">
insert into user values (null, #{name}, #{age})
</insert>
<update id="updateByIdXml">
update user set name = #{name} where id = #{id}
</update>
</mapper>
|
当处理完 selectUser 方法对应的标签后,得到的 Configuration 对象的 mappedStatement 信息为:
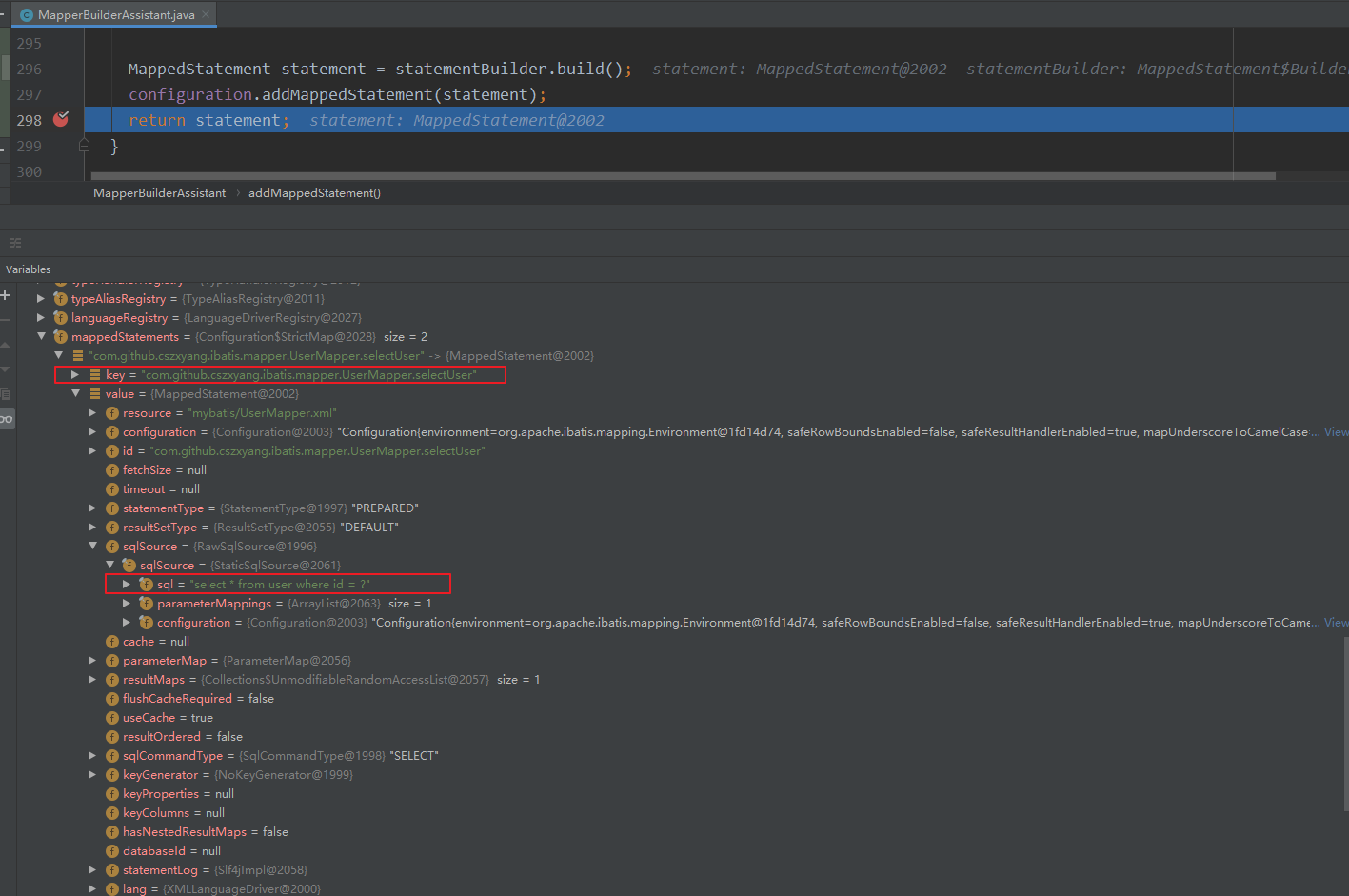
UserMapper 接口如下,其中定义了一个注解标识 SQL 方法与三个绑定 XML 文件的方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
public interface UserMapper {
// @Select("select * from t_user where id = #{id}")
User selectUser(Integer id);
@Update("update user set name = #{name} where id = #{id}")
int updateById(Integer id, String name);
int updateByIdXml(@Param("id") Integer id, @Param("name") String name);
int addUser(@Param("name") String name, @Param("age") Integer age);
}
|
ContainerMapper 接口如下,其中定义了一个绑定 XML 文件的方法。
1
2
3
|
public interface ContainerMapper {
Container listContainer(Integer id);
}
|
当所有的 mapper 的 XML 都解析完的时候,得到的 Configuration 对象的 mappedStatement 信息为:
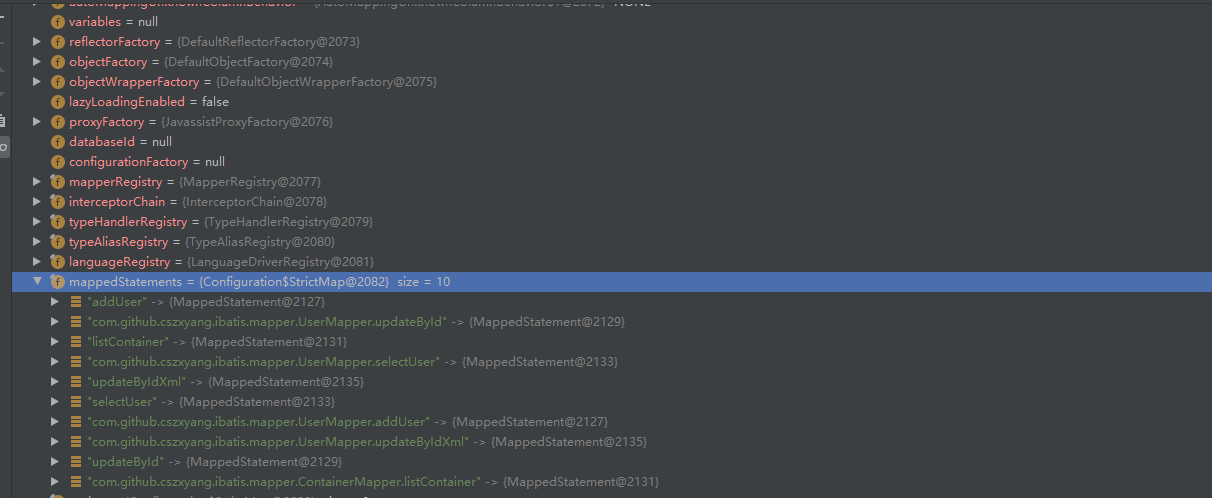
为什么一个方法有两个元素,分别为绝对形式与相对形式的,它们分别在哪个时机被使用?
Configuration 的 mappedStatements 是自定义的 HashMap 的子类 StrictMap,在往其中添加 MappedStatement 时,如果是类似 xxxMapper.xx 形式的方法标签,会获取一个简短的名称,看这个简短方法名是否存在对应的 MappedStatement,如果没有则会为之添加一个键值对,当然原来长的方法名也会添加进去。所以就会看到上面的现象,一个方法名往往对应在 mappedStatements 会有两份。
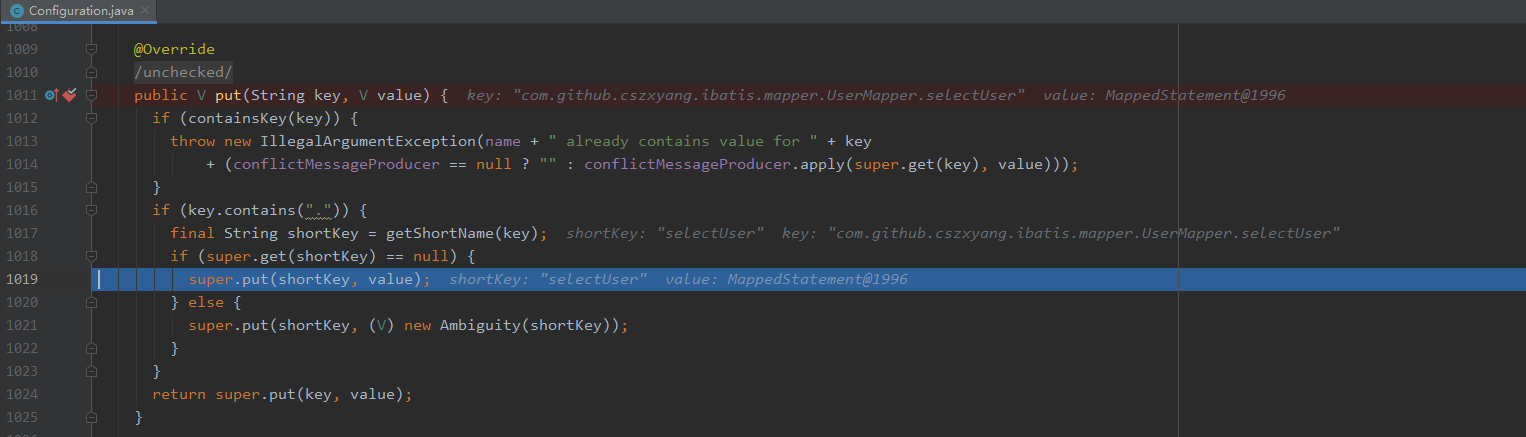
使用注解标识的 SQL 语句是在哪个时机被解析进 Configuration 的?
见下面的 Mapper 接口注册流程。
mapper 绑定
执行完 XMLMapperBuilder#configurationElement 方法,然后进入 bindMapperForNamespace 方法
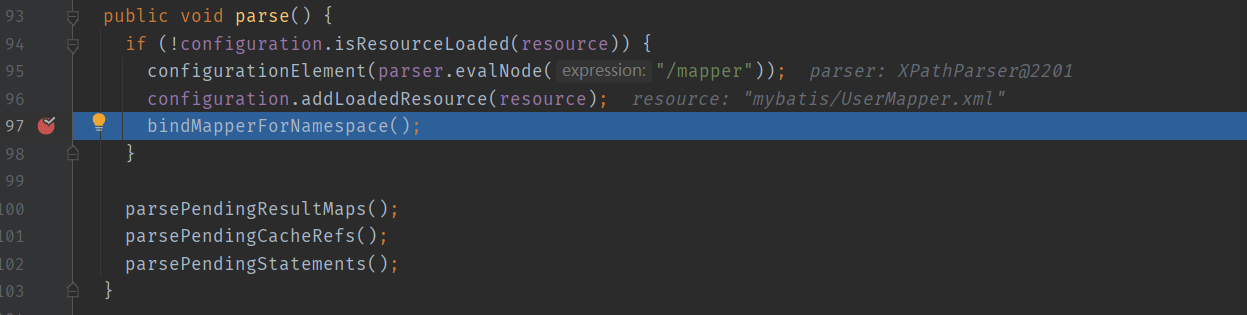
XMLMapperBuilder#bindMapperForNamespace 方法如果没有判断到 Configuration 没有 mapper,会调用 Configuration 的 addMapper 方法往其中注册 Mapper 接口信息。
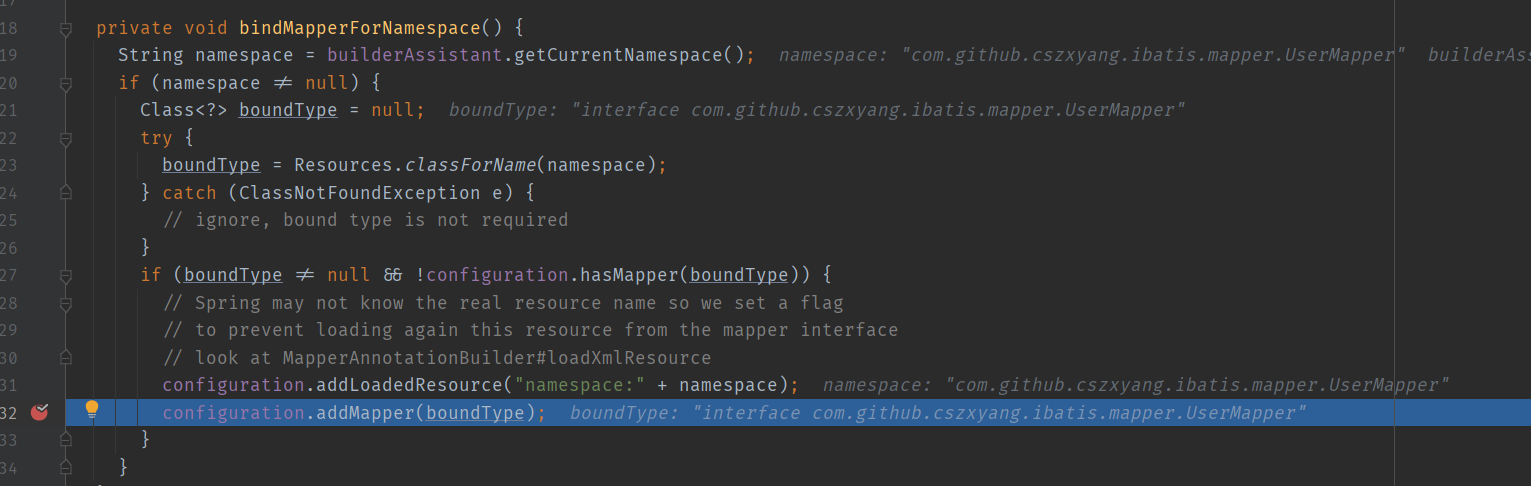
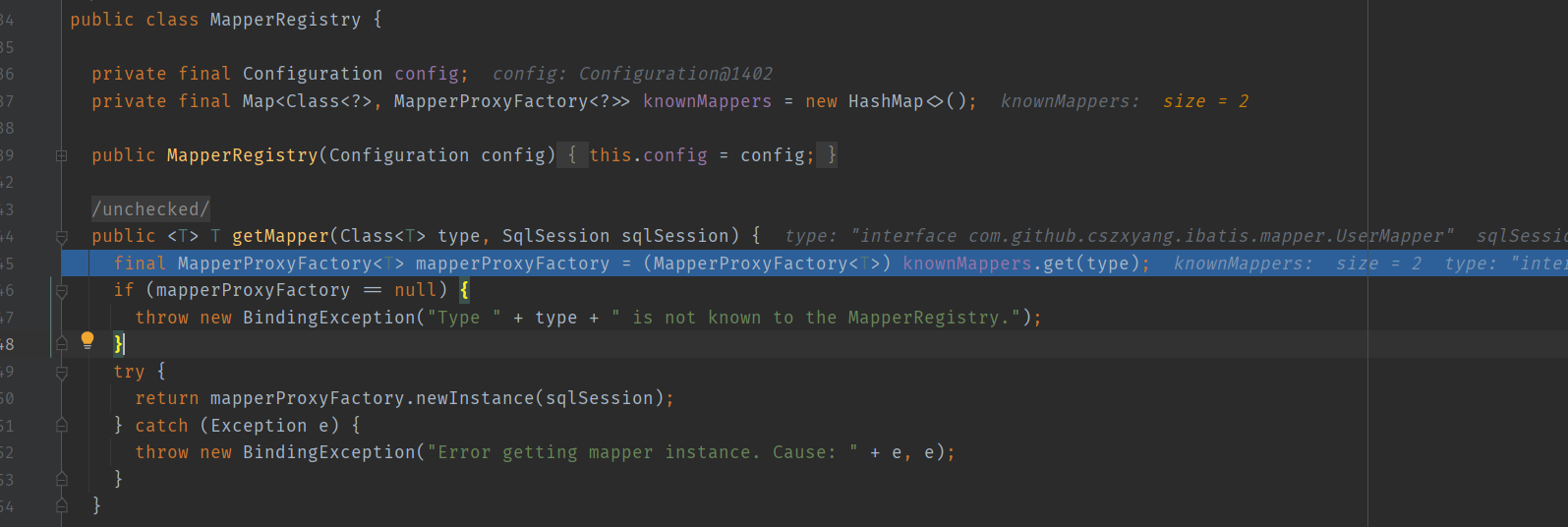
Configuration#addMapper 会调用 MapperRegistry#addMapper 方法,MapperRegistry 是 Configuration 维护的一个成员,按我理解是 “配置信息中的一部分,用于记录 mapper 注册信息”。
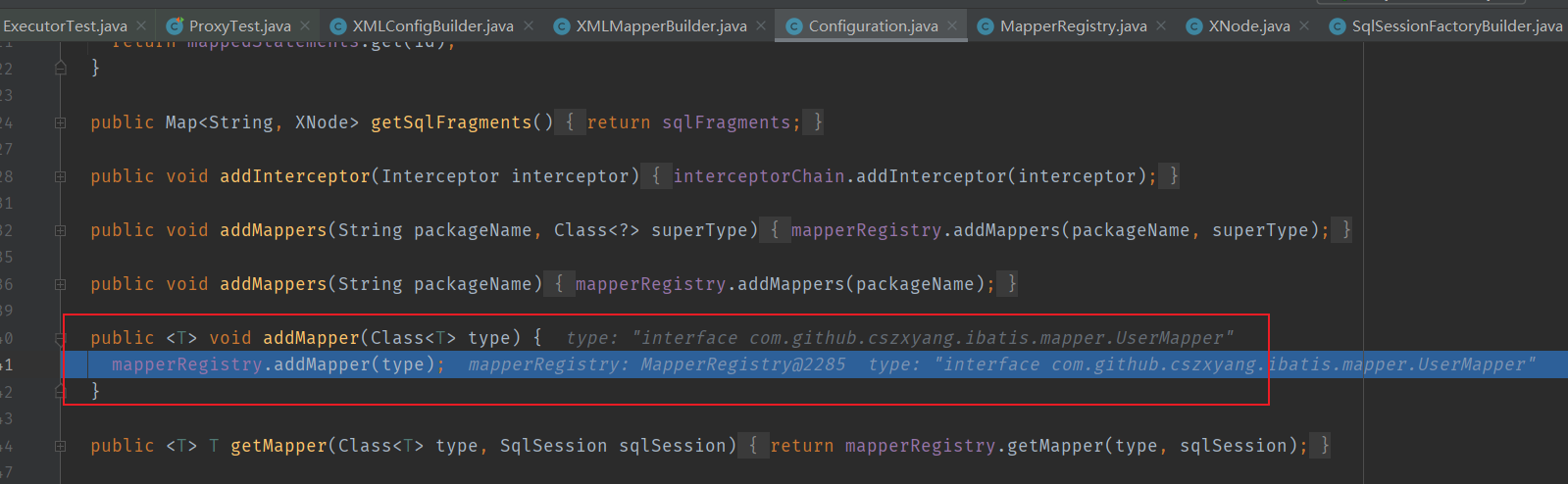
再看 MapperRegistry#addMapper 方法,入参是 Mapper 接口的 Class 信息,将它丢到其成员 private final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new HashMap<>(); 中,key 是 Class 对象引用,value 则是一个 MapperProxyFactory 对象,
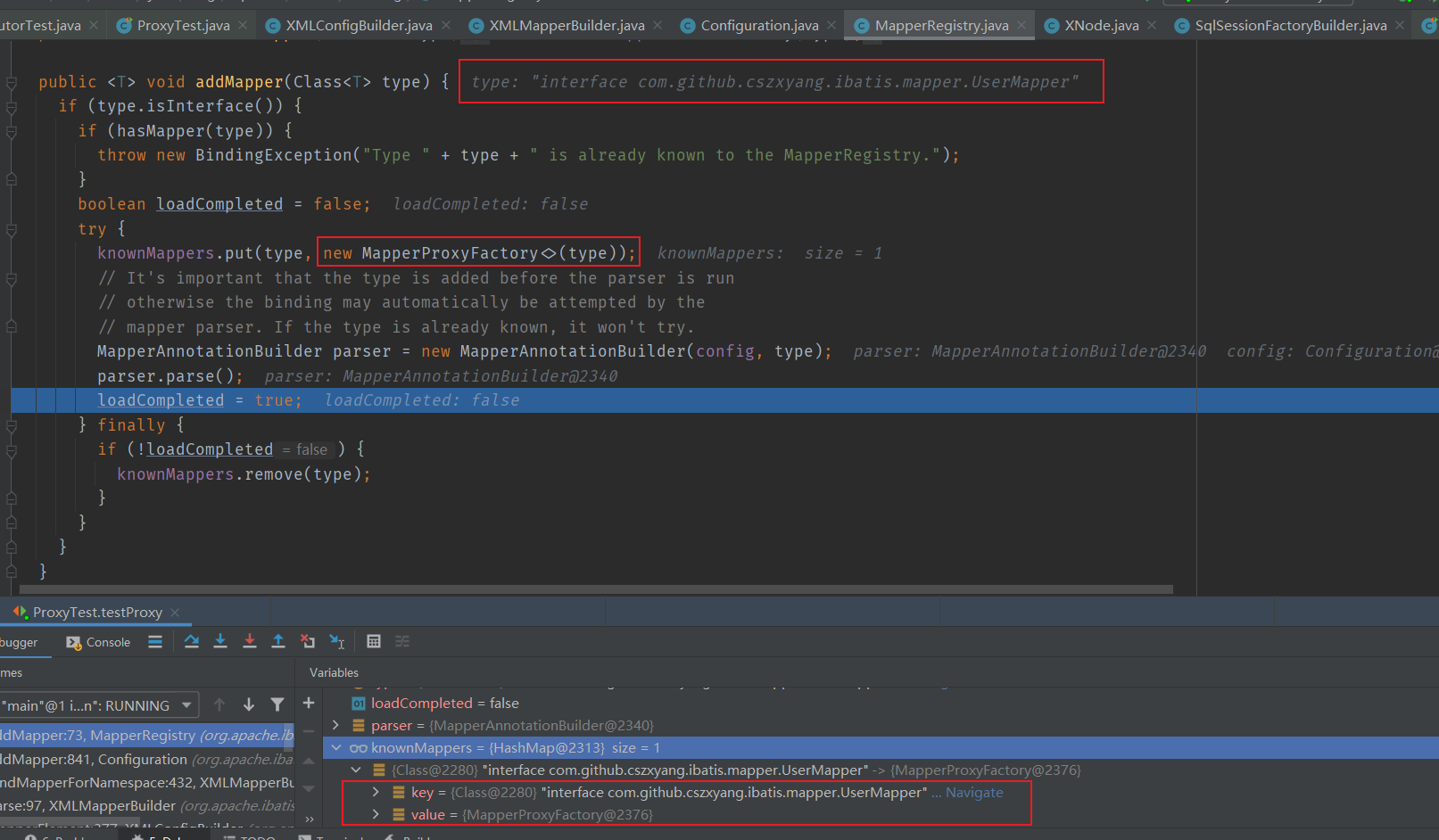
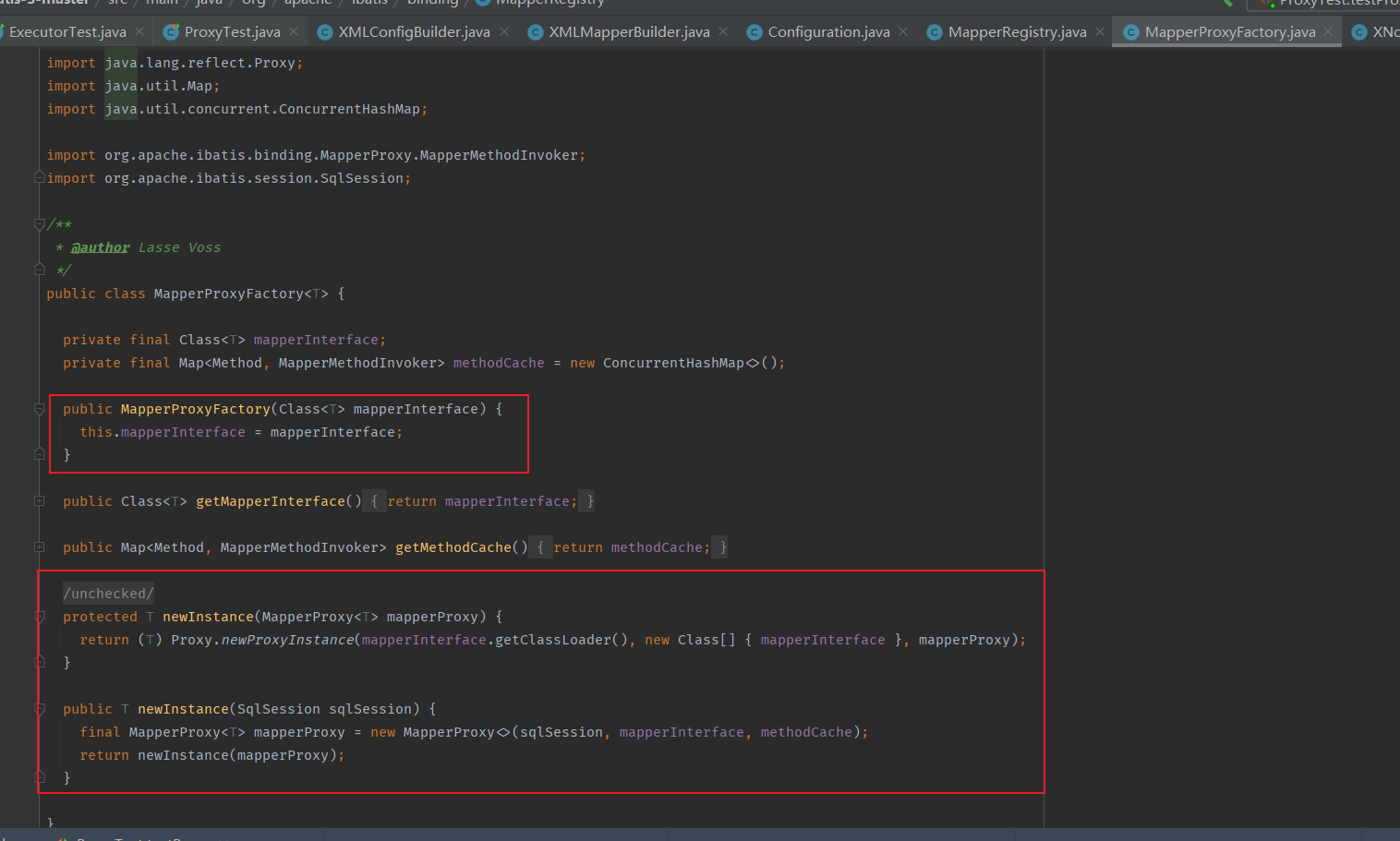
MapperProxyFactory 是所谓的代理对象生产工厂,其构造参数接收代理的接口的 Class 信息,然后需要创建代理对象时将调用 newInstance 方法。
注解 SQL 的解析
在 MapperAnnotationBuilder#parseStatement 方法中会处理 Mapper 中定义的每个方法,其中会调用 getAnnotationWrapper 方法判断这个方法上是否加有以下注解。
1
2
3
4
|
private static final Set<Class<? extends Annotation>> statementAnnotationTypes = Stream
.of(Select.class, Update.class, Insert.class, Delete.class, SelectProvider.class, UpdateProvider.class,
InsertProvider.class, DeleteProvider.class)
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
|
如果有注解的话就根据这个注解类型,解析出相应的 SQL 等信息,然后构建 MappedStatement 并添加到 Configuration 中。
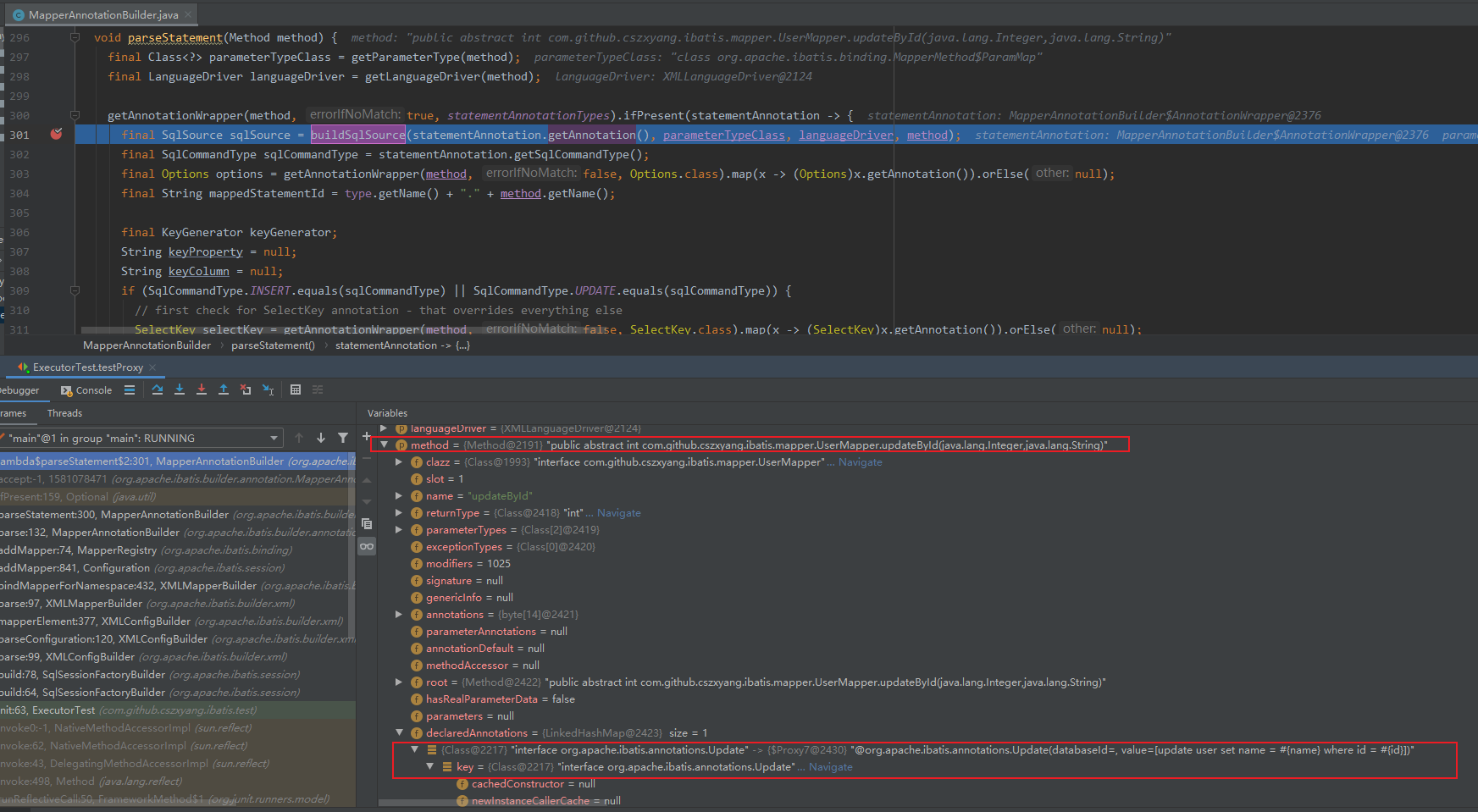
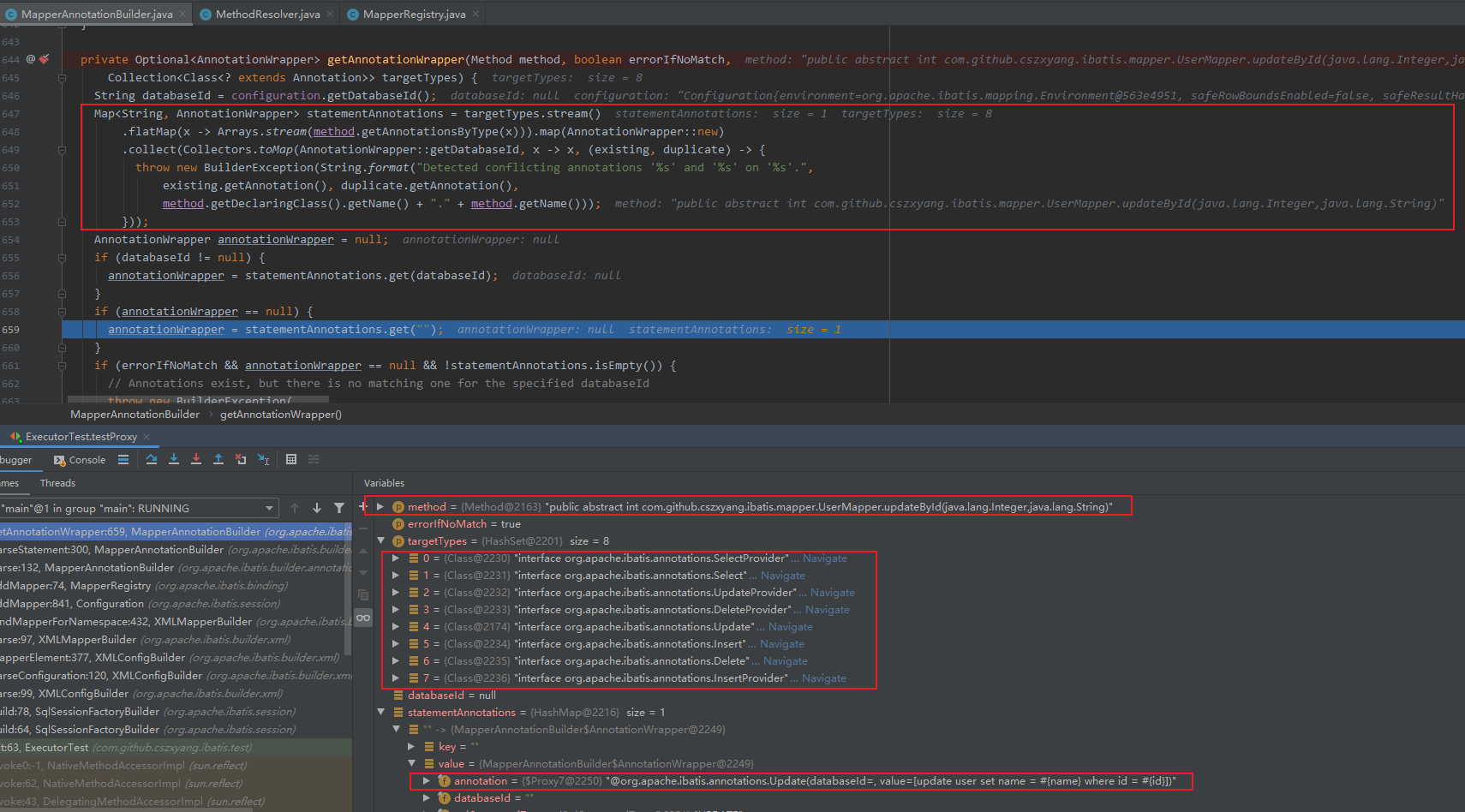
再看下 getAnnotationWrapper 方法,入参是上述的 statementAnnotationTypes 注解集合,其中包含 8 个注解类型,
-
遍历 statementAnnotationTypes,对于注解类型 x,有 .flatMap(x -> Arrays.stream(method.getAnnotationsByType(x))) 一句,method.getAnnotationsByType(x) 用来获取当前处理方法上加了 x 类型的注解,或许这里可以加多个相同类型的注解,所以 getAnnotationsByType 方法返回的一个 Annotation 数组,所以使用 Stream.of 并压平,然后每个 Annotation 对象转化为 AnnotationWrapper 对象,然后以 databaseId 为维度进行分组。
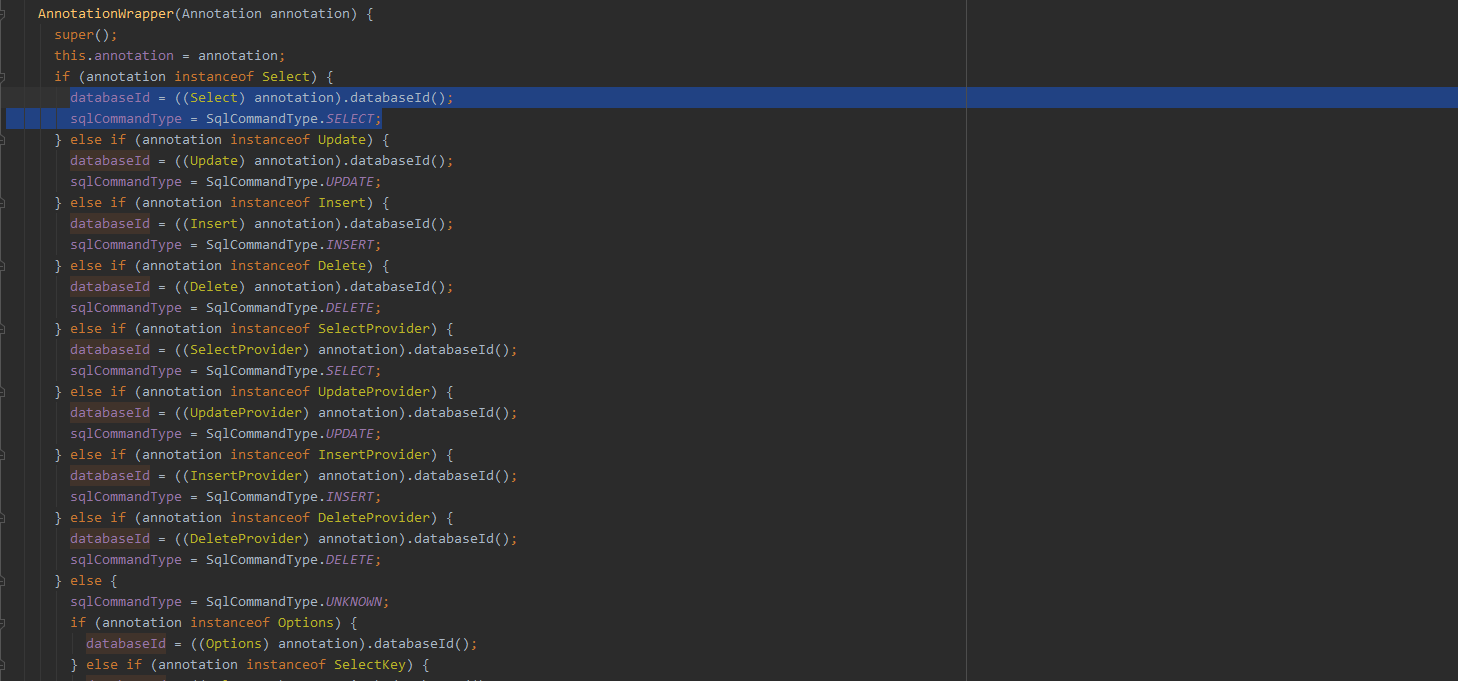
由于 Mybatis 支持多数据源,对于每个 SQL 语句都可以指定去哪个数据源执行,所以 Update、Select 等这一堆注解中都可以指定 databaseId 属性,然后 AnnotationWrapper 封装时也会囊括这个字段。
-
获取当前配置的数据源的 databaseId 对应的 AnnotationWrapper。
Mapper 代理对象的生成
跳进 SqlSession 的 getMapper 方法,
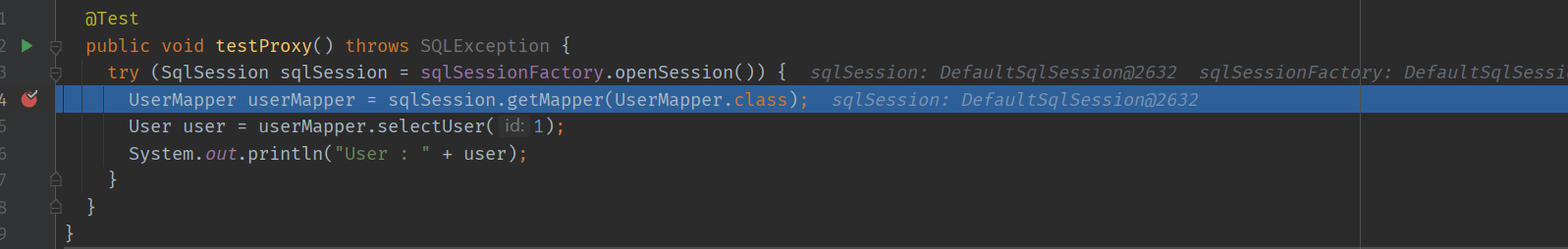
SqlSession 是根据 Configuration 来创建的,所以它会持有一个 Configuration 对象
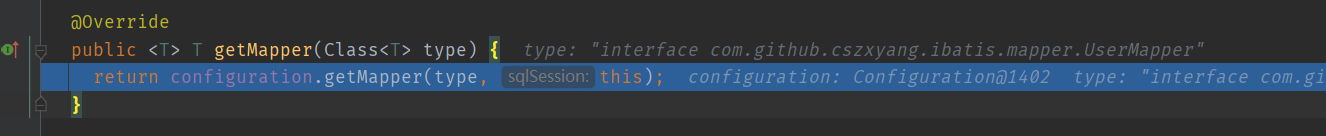
然后由于 Mapper 的配置信息时放在 Configuration 的 MapperRegistry 里面的,所以需要调用 MapperRegistry#getMapper 方法获取 Mapper 代理对象。
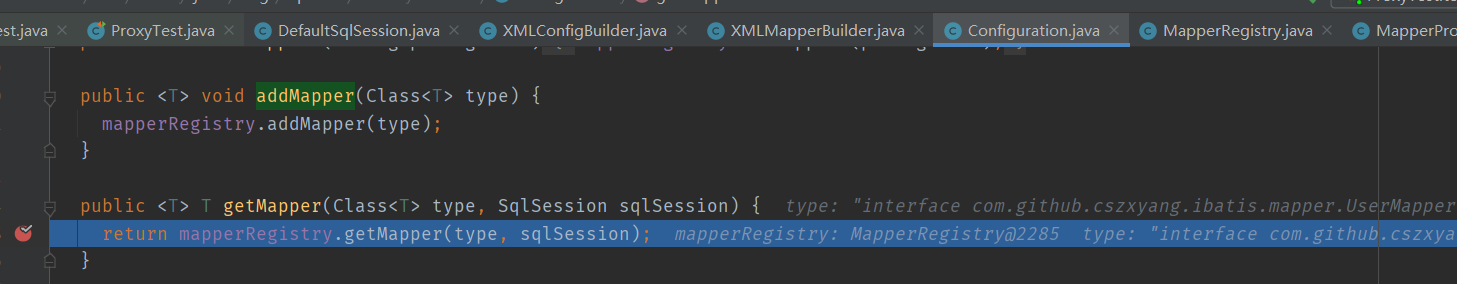
然后通过 Mapper 接口的 Class 信息拿到相应的 MapperProxyFactory 对象,然后调用其 newInstance 方法创建代理对象。
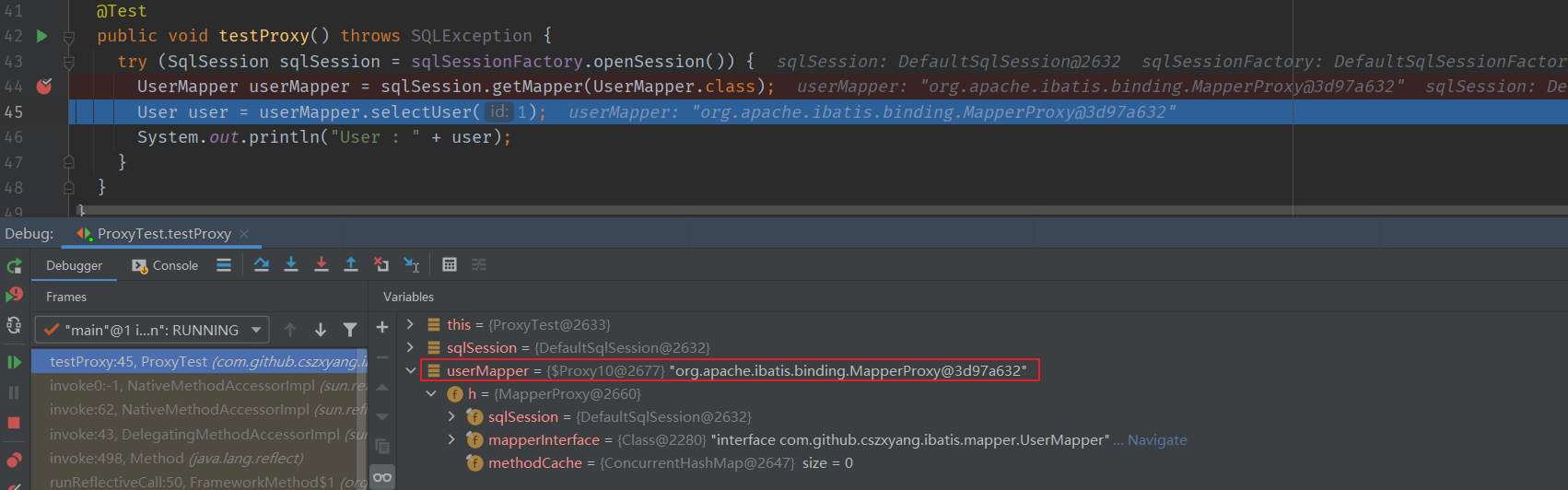
再回看 MapperProxyFactory#newInstance 方法,入参是 SqlSession 对象,根据 SqlSession 创建 MapperProxy 对象,然后通过 JDK 的动态代理技术创建 Mapper 接口的代理对象。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
|
通过 debug 信息可见,最后生成的 Mapper 接口实现是 MapperProxy 对象。
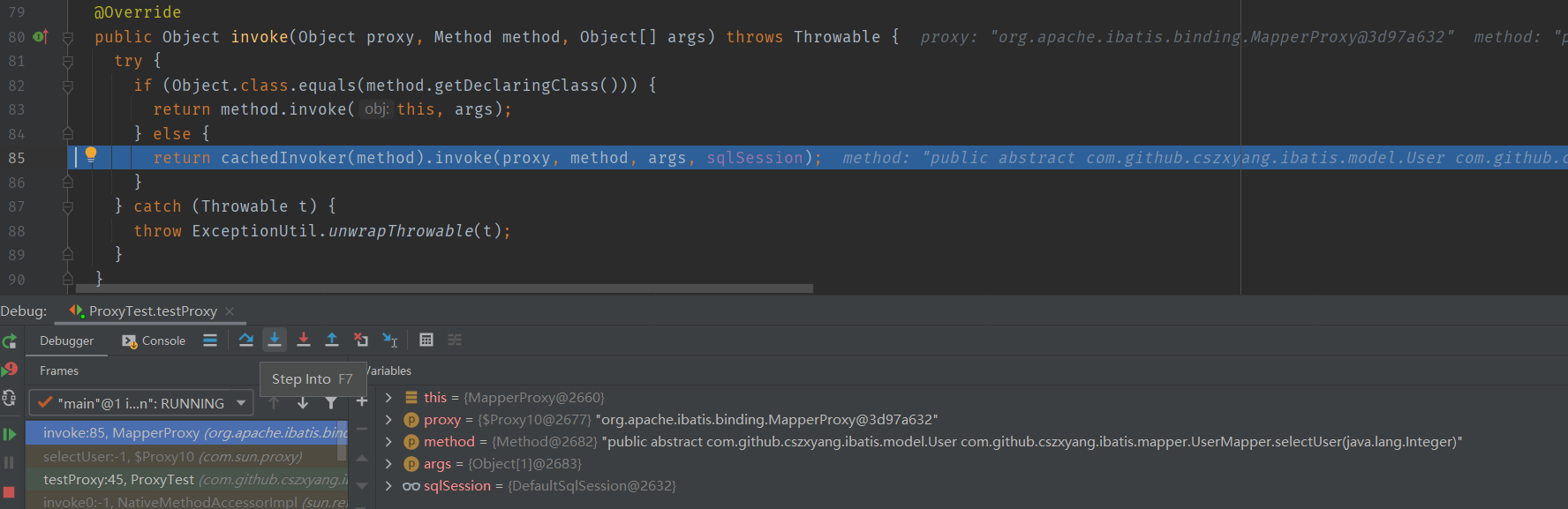
代理方法的触发
调用 mapper 接口的 selectUser 方法,将触发代理类 MapperProxy 中实现自 InvocationHandler#invoke 方法。invoker 方法会根据方法信息去缓存中获取对应的方法调用器,如果获取不到就默认创建一个 PlainMethodInvoker 对象。
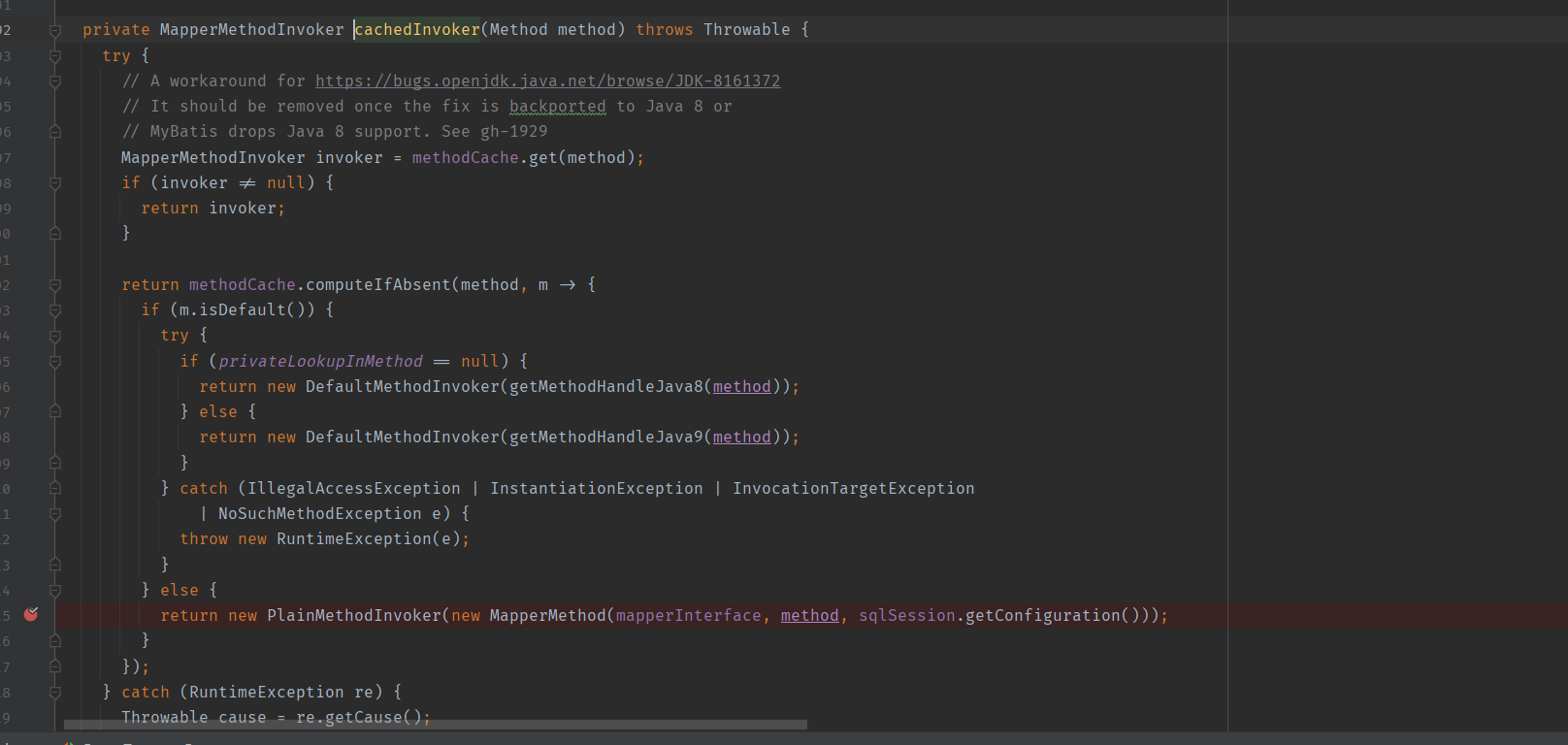
所以一般地 cachedInvoker 默认会返回一个 PlainMethodInvoker 对象,其中传入构造函数的参数是以 mapper 接口信息、触发的方法信息和 session 信息为参数构建的 MapperMethod 对象。
MapperMethod 构造时会初始化其 SqlCommand 和 MethodSignature 成员变量
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
public class MapperMethod {
private final SqlCommand command;
private final MethodSignature method;
public MapperMethod(Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) {
this.command = new SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method);
this.method = new MethodSignature(config, mapperInterface, method);
}
}
|
下面是 SqlCommand 的构造函数,其 SqlCommandType 成员会记录对应 SQL 命令的类型,如 UNKNOWN, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, SELECT, FLUSH 等。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
public static class SqlCommand {
private final String name;
private final SqlCommandType type;
public SqlCommand(Configuration configuration, Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method) {
final String methodName = method.getName();
final Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass();
MappedStatement ms = resolveMappedStatement(mapperInterface, methodName, declaringClass,
configuration);
if (ms == null) {
if (method.getAnnotation(Flush.class) != null) {
name = null;
type = SqlCommandType.FLUSH;
} else {
throw new BindingException("Invalid bound statement (not found): "
+ mapperInterface.getName() + "." + methodName);
}
} else {
// 记录 MappedStatement 的 id,后续根据 id 获取到 Configuration 中的 MappedStatement
name = ms.getId();
type = ms.getSqlCommandType();
if (type == SqlCommandType.UNKNOWN) {
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + name);
}
}
}
}
|
MethodSignature 用来维护 Mapper 方法对应的出入参等签名信息。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
public static class MethodSignature {
private final boolean returnsMany;
private final boolean returnsMap;
private final boolean returnsVoid;
private final boolean returnsCursor;
private final boolean returnsOptional;
private final Class<?> returnType;
private final String mapKey;
private final Integer resultHandlerIndex;
private final Integer rowBoundsIndex;
private final ParamNameResolver paramNameResolver;
public MethodSignature(Configuration configuration, Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method) {
Type resolvedReturnType = TypeParameterResolver.resolveReturnType(method, mapperInterface);
if (resolvedReturnType instanceof Class<?>) {
this.returnType = (Class<?>) resolvedReturnType;
} else if (resolvedReturnType instanceof ParameterizedType) {
this.returnType = (Class<?>) ((ParameterizedType) resolvedReturnType).getRawType();
} else {
this.returnType = method.getReturnType();
}
this.returnsVoid = void.class.equals(this.returnType);
this.returnsMany = configuration.getObjectFactory().isCollection(this.returnType) || this.returnType.isArray();
this.returnsCursor = Cursor.class.equals(this.returnType);
this.returnsOptional = Optional.class.equals(this.returnType);
this.mapKey = getMapKey(method);
this.returnsMap = this.mapKey != null;
this.rowBoundsIndex = getUniqueParamIndex(method, RowBounds.class);
this.resultHandlerIndex = getUniqueParamIndex(method, ResultHandler.class);
this.paramNameResolver = new ParamNameResolver(configuration, method);
}
}
|
再回到 MapperProxy#invoke 方法的逻辑,获取到 PlainMethodInvoker 对象后,会调用 PlainMethodInvoker#invoke 方法,实际上是 MapperMethod#execute 方法。
SQL 指令执行
MapperMethod#execute 方法代码如下,先判断相应方法的 SQL 指令的类型,根据不同的 DML 指令类型执行不同的处理。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
|
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional()
&& (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
|
以查询为例,SqlSession#selectOne 会调用 DefaultSqlSession#selectList 方法,其中会调用 Configuration#getMappedStatement 方法
Configuration#getMappedStatement 是根据 XML 标签中的 id 获取到具体的 statement,前面在 mapper 的 XML 的解析中介绍到 Mybatis 已经将 Mapper 中的信息读取到了 Configuration 里面了,所以这里能够直接拿到具体的配置在 XML 文件中的 SQL 语句,从而调用 JDBC 就能执行相应的指令
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
public MappedStatement getMappedStatement(String id, boolean validateIncompleteStatements) {
if (validateIncompleteStatements) {
buildAllStatements();
}
return mappedStatements.get(id);
}
|

























